Posts by Veridify Security
The Cost of a Cyber Breach in Smart Buildings: Beyond Data Loss
Quick Summary A cyber breach in building automation can inflict far greater damage than lost data. Beyond IT, BAS attacks can bring down HVAC, disable access control, spike utility costs, disrupt tenant operations, and tarnish reputation. Real-world data shows that breaches cost millions — and when smart buildings are involved, that number can skyrocket. Introduction…
Read MoreTop BAS/BMS Protocol Vulnerabilities
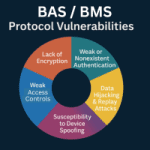
Quick Summary Legacy BAS/BMS protocols share common vulnerabilities, including no encryption, weak authentication, spoofing risks, replay attacks, and weak access controls. These flaws expose HVAC, lighting, and access systems to manipulation and disruption. Zero Trust, encryption, and device-level authentication can secure even legacy systems without costly replacement. Introduction Building automation systems (BAS) connect and control…
Read MoreCybersecurity Awareness Month 2025
October is Cybersecurity Awareness Month 2025 Cybersecurity Awareness Month 2025 is a collaboration between government and private industry to raise awareness about digital security and empower everyone to protect their personal data from digital forms of crime. The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency (CISA) and the National Cybersecurity Alliance partner to create resources and communications for…
Read MoreFrom Air Gaps to Always Connected: The Evolution of Smart Building Cyber Threats
Quick Summary Smart building cyber threats have evolved alongside the shift from isolated, air-gapped BAS to always-connected systems. While connectivity boosts efficiency, it also exposes HVAC, lighting, and access controls to ransomware, weak protocols, and IT/OT convergence risks. To defend against these threats, facility managers must adopt Zero Trust and device-level security to ensure resilience.…
Read MoreThe Hidden Cyber Risks Inside HVAC, Lighting, and Access Control Systems
Quick Summary HVAC, lighting, and access control systems may appear harmless but can be exploited to cause serious operational, financial, and safety issues. These “hidden” risks arise from insecure protocols, lack of authentication, and poor segmentation. By adopting Zero Trust principles and device-level protection, facility managers and building operators can turn vulnerable systems into secure…
Read MoreWhy Building Automation Systems Are the New Cybersecurity Target
Quick Summary Building Automation Systems (BAS) are increasingly targeted by cybercriminals because they manage critical building functions such as HVAC, lighting, elevators, and access controls. Once considered safe due to isolation, BAS are now internet-connected and often insecure by design, making them gateways to both operational disruption and corporate IT networks. As cyberattacks on smart…
Read MoreZero Trust for OT Security: The Last Line of Defense
Quick Summary Traditional firewalls were never designed to meet the unique security needs of Operational Technology (OT) environments. While they are effective at blocking outside threats, once an attacker breaches the perimeter, devices inside remain vulnerable. Real-world incidents like Colonial Pipeline, Triton malware, and ransomware in building automation highlight how attackers exploit insecure OT protocols…
Read MoreSecuring M2M Communication and Devices for Industrial IoT
Quick Summary Machine-to-Machine (M2M) devices drive efficiency and automation in Industrial IoT (IIoT), but they also introduce serious cybersecurity risks. This article explores common vulnerabilities, best practices, emerging technologies, and actionable steps to secure M2M systems from evolving threats. Why M2M Security Can’t Be an Afterthought Industrial IoT usage is growing fast, from smart factories…
Read MoreOvercoming Niagara Framework Cyber Vulnerabilities
Key Points Comprehensive Vulnerability Mitigation: DOME encrypts all device communications, enforces unique cryptographic identities, blocks unauthorized actions, and prevents lateral movement even on flat networks—addressing risks like unencrypted data, credential hijacking, privilege escalation, and insecure configurations. Zero Trust at the Endpoint: Every enrolled device must authenticate and follow strict, policy-based access rules, ensuring only explicitly…
Read MoreFuture-Proofing OT Cybersecurity
Key Points OT Cybersecurity Faces Unique Challenges: Operational technology networks are often outdated, lack operating systems, span wide geographies, and weren’t designed for connectivity—making them vulnerable and hard to secure. Existing IT-Based Solutions Fall Short: Current cybersecurity tools focus on monitoring and alerting rather than proactive protection, leading to alert fatigue and leaving OT…
Read More