Zero Trust
Zero Trust for OT Security: The Last Line of Defense
Quick Summary Traditional firewalls were never designed to meet the unique security needs of Operational Technology (OT) environments. While they are effective at blocking outside threats, once an attacker breaches the perimeter, devices inside remain vulnerable. Real-world incidents like Colonial Pipeline, Triton malware, and ransomware in building automation highlight how attackers exploit insecure OT protocols…
Read MoreFuture-Proofing OT Cybersecurity
Key Points OT Cybersecurity Faces Unique Challenges: Operational technology networks are often outdated, lack operating systems, span wide geographies, and weren’t designed for connectivity—making them vulnerable and hard to secure. Existing IT-Based Solutions Fall Short: Current cybersecurity tools focus on monitoring and alerting rather than proactive protection, leading to alert fatigue and leaving OT…
Read MoreZero Trust Security for Microgrids and Energy Control Systems
Key Points Growing Cyber Risk in Microgrids: The distributed nature, two-way data flows, and device diversity in microgrids greatly expand the attack surface, making traditional perimeter-based security insufficient. Limitations of Legacy Security: Older “verify then trust” models lack device-level authentication/encryption, leaving systems vulnerable if an insider device is compromised and failing to protect at Purdue…
Read MoreZero Trust Security for Legacy OT Devices
Key Points Legacy OT Challenges: Many older OT systems use insecure protocols, lack modern security features, and have limited hardware resources—making them difficult to protect using traditional cybersecurity methods. Zero Trust Integration Options: Three primary methods exist—device replacement (costly), software-defined networking (limited protection), and security overlays (most effective and non-intrusive), with overlays offering encryption and…
Read MoreZero Trust vs Remote Access VPN for Building Control Systems
Zero Trust architecture fundamentally transforms how organizations secure their building automation networks by addressing the inherent vulnerabilities of traditional remote access VPN-based security. Key Points VPNs Grant Broad Access; Zero Trust Enforces Least Privilege: VPNs give authenticated users full network access, while Zero Trust limits each user or device to only the specific resources needed,…
Read MoreHow Zero Trust Enhances the Security of Building Control Systems
Key Points Minimizes Attack Surface: Replaces location-based trust with granular access controls, reducing the chance of a single breach spreading across interconnected BAS components. Prevents Lateral Movement: Uses micro-segmentation to isolate workloads and resources, containing threats within compromised segments. Continuous Verification & Least Privilege: Continuously authenticates and authorizes users/devices while limiting each to only the…
Read MoreBuilding Automation Endpoint Protection Is Critical for Cybersecurity
Building automation systems (BAS), now highly-connected to the internet, have transformed how the infrastructure of residential, commercial, and industrial properties is managed and optimized. From heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems to lighting, security, life safety, and power distribution, these systems are now smart, centralized, and increasingly automated. While this level of convenience and…
Read MoreZero Trust for OT Security: Cyber Defense Inside the Perimeter
Inside the Perimeter Defense is a Crucial Part of Defense in Depth for OT Security Firewalls for OT Security Perimeter Defense Firewalls are essential components of network security, acting as perimeter defenses that control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. However, they are not without their own set of potential security…
Read MoreProtecting Building OT Systems from Cyber Threats
Operational Technology (OT) systems in buildings, which include HVAC, lighting, access control, and other critical infrastructure, are increasingly becoming targets for cyber threats. The rise in attacks on these systems underscores the importance of robust cybersecurity measures to protect them. Here’s a look at how to safeguard building OT systems from cyber threats. Understanding the…
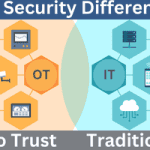
Read MoreKey Differences Between Zero Trust OT Security and Traditional IT Security
How is Zero Trust for OT Security Different from Traditional IT Security? Zero Trust for operational technology (OT) security differs significantly from traditional IT security models in several ways. Here are some key differences: Security Method Traditional IT Security Zero Trust OT Security Trust Model – Assumes that everything inside the network can be trusted.…
Read More