Securing M2M Communication and Devices for Industrial IoT
Quick Summary
Machine-to-Machine (M2M) devices drive efficiency and automation in Industrial IoT (IIoT), but they also introduce serious cybersecurity risks. This article explores common vulnerabilities, best practices, emerging technologies, and actionable steps to secure M2M systems from evolving threats.
Why M2M Security Can’t Be an Afterthought
Industrial IoT usage is growing fast, from smart factories to remote healthcare devices, yet every connected sensor, robot, and controller is a potential cyber entry point. A single breach could halt production lines, endanger worker safety, or compromise patient care. The question isn’t whether you should secure M2M communication, it’s whether you can afford not to.
Understanding M2M Communication
What is M2M Communication?
Machine-to-Machine communication enables devices to exchange data without human input, the backbone of automation in IIoT.
M2M Use Cases
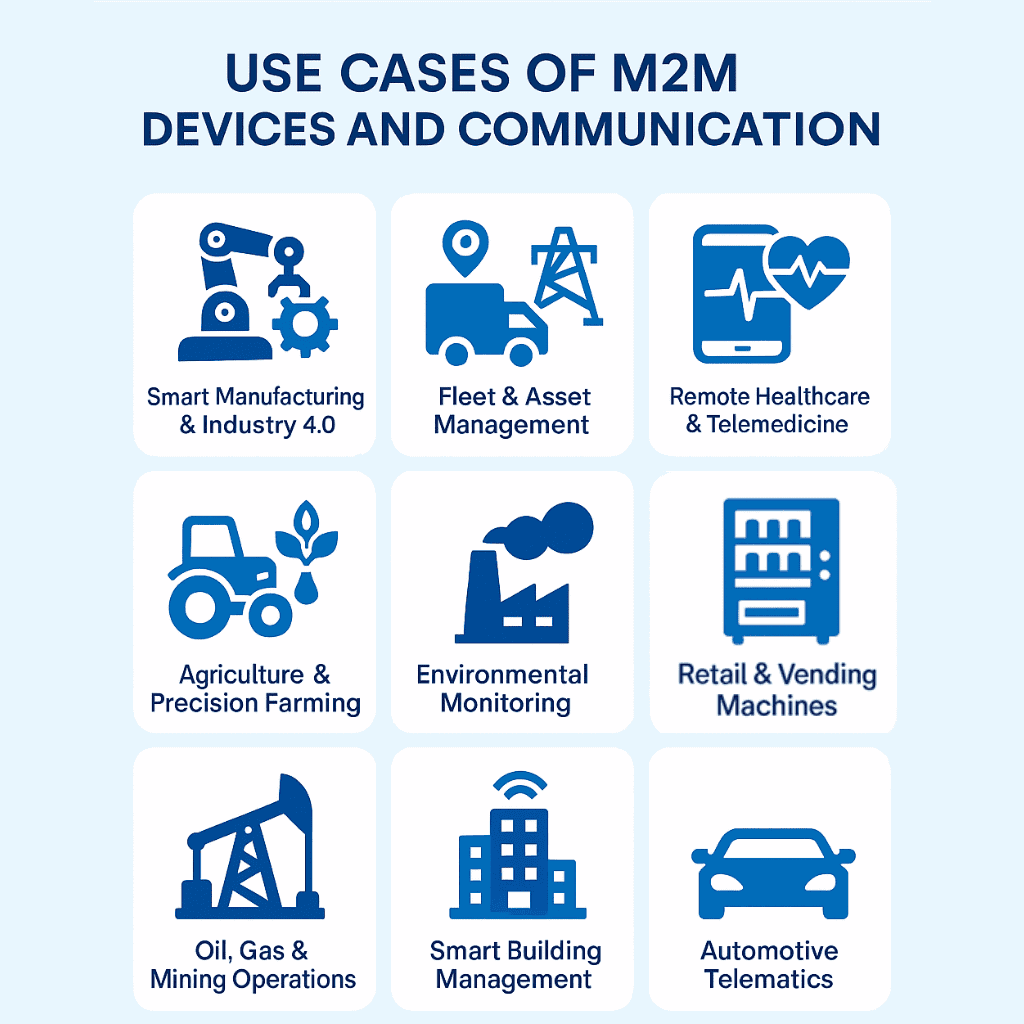
Below is a visual map of 10 high-impact M2M applications across industries:
- Smart Manufacturing & Industry 4.0 – Automated assembly lines where machines exchange performance data for real-time process adjustments.
- Fleet & Asset Management – GPS-enabled tracking devices sending location, fuel usage, and maintenance data to logistics platforms.
- Smart Grids & Energy Management – Connected meters and transformers optimizing power distribution and detecting outages.
- Remote Healthcare & Telemedicine – Medical devices transmitting patient vitals to healthcare providers for real-time monitoring.
- Agriculture & Precision Farming – Soil sensors and weather stations communicating irrigation and crop health data to automated systems.
- Environmental Monitoring – Air and water quality sensors sending real-time pollution and hazard alerts to authorities.
- Smart Building Management – HVAC, lighting, and security systems coordinating energy use and occupant comfort without human intervention.
- Automotive Telematics – Vehicles sending diagnostic, performance, and safety alerts to service centers and manufacturers.
- Oil, Gas & Mining Operations – Remote sensors on rigs or equipment providing operational status and safety alerts.
- Retail & Vending Machines – Smart vending units reporting stock levels, sales data, and maintenance needs to central systems.
Key Benefits of M2M Devices and Communication
1. Increased Operational Efficiency
M2M systems automate data exchange between devices, reducing the need for manual intervention.
- Machines adjust operations in real time based on sensor inputs.
- Downtime is minimized because adjustments happen without human delay.
2. Predictive Maintenance & Reduced Downtime
By monitoring equipment health continuously, M2M devices can detect early signs of wear or malfunction.
- Maintenance is performed only when needed, lowering costs.
- Reduces unexpected failures that can halt production.
3. Real-Time Decision-Making
Data flows instantly from devices to control systems or analytics platforms.
- Enables rapid adjustments in manufacturing, logistics, or energy distribution.
- Improves responsiveness to environmental or operational changes.
4. Cost Savings
Automation and predictive analytics help lower operational expenses.
- Reduced labor costs due to fewer manual checks.
- Lower energy consumption through optimized processes.
5. Improved Accuracy & Reduced Human Error
Devices exchange and process data directly, minimizing the chance of mistakes from manual entry.
- Particularly valuable in precision manufacturing, medical monitoring, and environmental sensing.
6. Enhanced Asset Tracking & Management
In logistics, transportation, and supply chains, M2M provides real-time tracking of goods, vehicles, and equipment.
- Improves security and inventory control.
- Optimizes asset utilization.
7. Better Resource Utilization & Sustainability
M2M communication allows smarter energy, water, and raw material usage.
- Examples: Smart grids that balance power demand; irrigation systems that water only when soil moisture is low.
8. Scalability for Expanding Operations
M2M networks can easily integrate new devices without overhauling infrastructure.
- Ideal for businesses planning growth or diversification.
Vulnerabilities in M2M Communication
Key M2M Security Risks
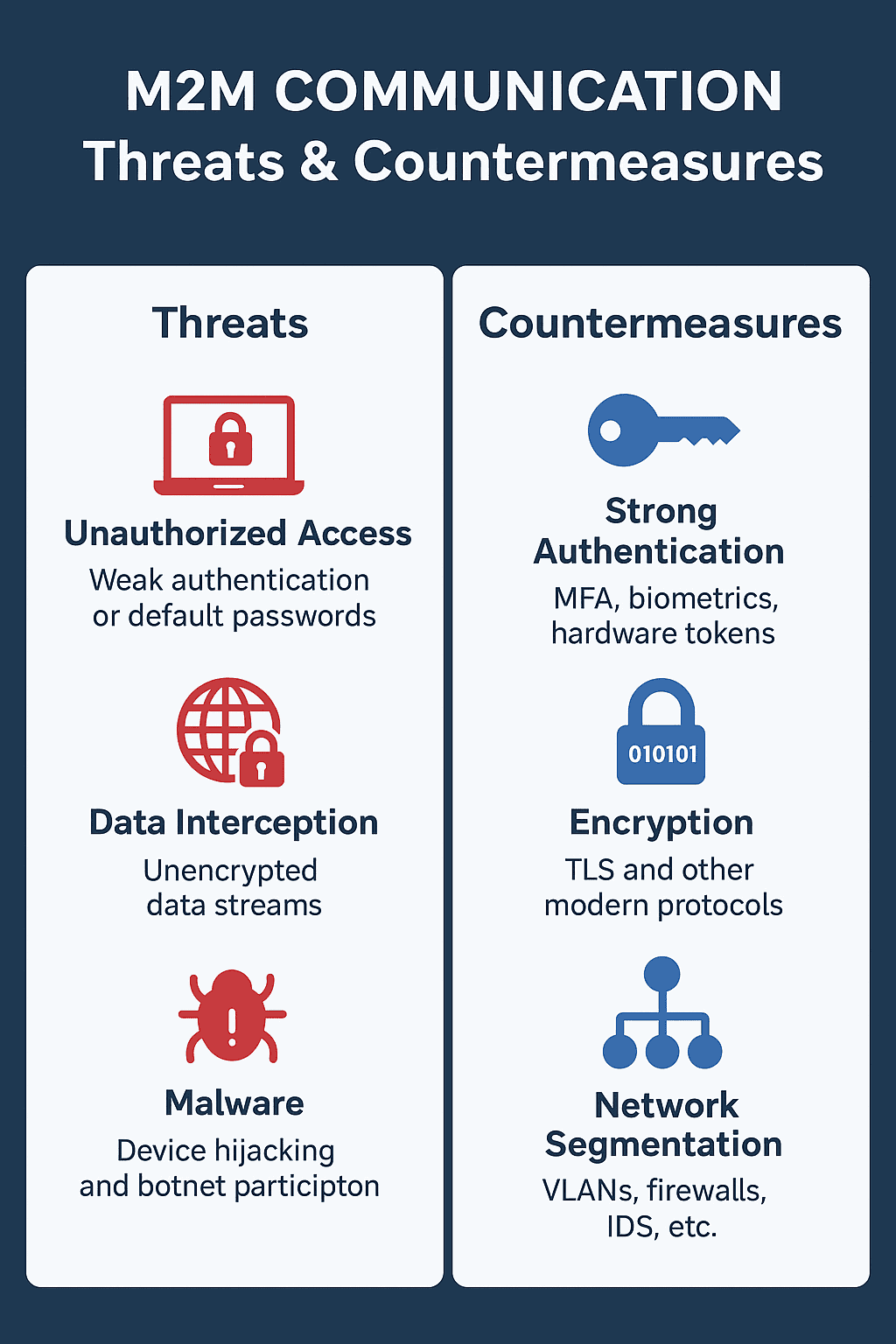
- Unauthorized Access: Weak authentication or default passwords
- Data Interception: Unencrypted data streams
- Insecure Protocols: Outdated communication standards
Common Threats
- MitM Attacks: Data interception or command manipulation
- DoS Attacks: Disruption of critical operations
- Malware: Device hijacking and botnet participation
Securing M2M Communication
Best Practices
- Strong Authentication: Multi-factor, biometrics, hardware tokens
- Encryption: TLS and other modern protocols, including NIAT-approved Quantum-Ready methods
- Patch Management: Automated updates for all devices
Secure Protocols
- Use IoT-optimized secure protocols like MQTT over TLS or CoAP with DTLS.
Network Segmentation
- VLAN isolation
- Firewalls & Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Device & Application Hardening
- Disable unused ports/services
- Implement secure boot processes
The Future of M2M Security
Emerging Technologies
- AI/ML: Real-time anomaly detection
- Blockchain: Immutable transaction records and root-of-trust for device authenticity
Building an M2M Security Culture
- Ongoing employee training
- Regular incident response drills
Key Takeaways
- M2M is critical for IIoT success but comes with high security stakes.
- Security must be multi-layered covering authentication, encryption, and segmentation.
- Emerging tools like AI and blockchain will play a bigger role in defense.
- A proactive security culture can mitigate most preventable breaches.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is M2M communication in IoT?
A: Machine-to-Machine communication is the automated data exchange between devices without human input, used in IIoT for efficiency and automation.
Q2: How can you secure M2M communication?
A: Use strong authentication, encrypt all transmissions, update devices regularly, and segment networks.
Q3: What are the biggest security risks in M2M systems?
A: Unauthorized access, data interception, insecure protocols, and malware infections.
Q4: Why is encryption important in M2M?
A: Encryption prevents hackers from intercepting or manipulating data between devices.
Q5: What role does AI play in M2M security?
A: AI can detect anomalies, predict threats, and automate incident responses in real time.
—
Blog Post Summary – All of our posts listed on one page